Nagendra Chaturvedi Lab

The main focus of Dr. Nagendra Chaturvedi's lab is to identify the key tumorigenic pathways and drivers in the most aggressive forms of medulloblastoma (MB) and neuroblastoma (NB) pediatric tumors and target those pathways for the development of therapies. The lab's current areas of interest include:
- Identifying oncogenic drivers and creating new in vitro and in vivo models
- Dissecting the molecular mechanisms of tumor progression and metastasis
- Small molecule therapeutics (in vitro and in vivo evaluation of single and combined drug approaches)
- Stem cell biology
- Epigenetic regulation of pediatric cancers
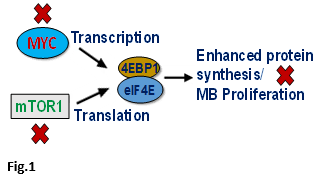
Targeting an Enhanced Protein Synthesis pathway in MYC-driven MB: One of Dr. Chaturvedi's studies identified that increased activation or overexpression of the protein synthesis pathway plays a key role in the progression and resistance of the highly aggressive MYC-oncogene amplified form of MB. In this study, he found that MYC transcription factor and mTOR translation signaling cooperate with each other to enhance protein synthesis, leading to increased proliferation. Therefore, using genetic and pharmacologic approaches in vitro and in vivo, his lab targeted these pathways together and found that combined inhibition of MYC transcription and mTOR signaling has a synergistic anti-tumor effect against MYC-driven medulloblastoma (Fig.1).
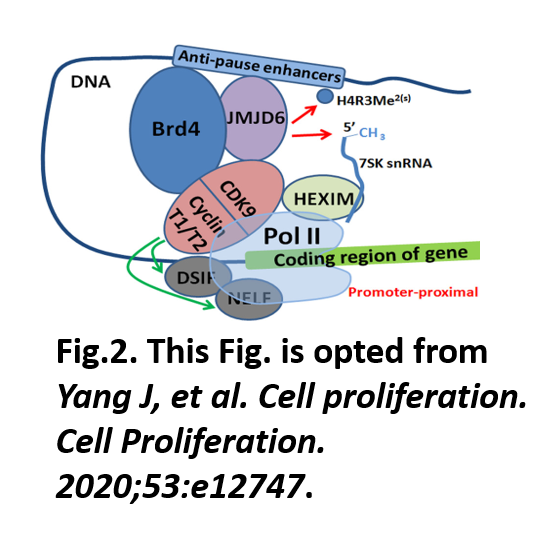
JMJD6 as a Novel Regulator of MYC-driven MB Tumorigenesis: Dysregulation of epigenetic pathways is very common in pediatric cancers, including MB. In another study, the Chaturvedi lab discovered that JMJD6, an epigenetic enzyme, can act as a powerful regulator of MYC-driven MB tumorigenesis. His lab found that JMJD6 is overexpressed in MB and positively associates with MYC expression. It not only overexpresses but also associates with poor clinical outcomes in MB. We also find that JMJD6 loss in MYC-driven MB cells leads to decreased cell proliferation and the induction of apoptosis, suggesting that JMJD6 is a potential therapeutic target in MB. JMJD6 is a member of the jumonji C domain-containing family of proteins and has arginine demethylase and lysyl hydroxylase activities that modify histone and non‐histone proteins. It has been shown that JMJD6 associates well with super-enhancer mediated gene transcription. As a histone arginine demethylase, JMJD6 upregulates target gene transcription by forming a protein complex with BET-protein BRD4 and demethylating histone H4 at target gene anti-pause enhancers leading to RNA polymerase II release from promotor-proximal pause region and gene transcription (Fig. 2). Dr. Chaturvedi's preliminary data indicate that this control of JMJD6 might have roles in the transcription regulation of MYC or other oncogenes that can contributes to MB tumorigenesis. So, currently, his lab is working on dissecting how this epigenetic mechanism(s) via JMJD6 can regulate certain oncogenes and can be targeted for MB therapeutics.
Lab contact information:
Lied Transplant Center
11732 Nebraska Medical Center
Omaha, Nebraska 68198-7627
Email: nchaturvedi@unmc.edu
Phone: 402-559-4163
Lab Features
Nagendra Chaturvedi, PhD (Assistant Professor)
Erin McIntyre, MS (Research Coordinator)
Gracey Alexander, BS (Research Technologist)
- Development of tumor mouse models, including intracranial/intracerebellar injections
- Cell culture and gene transfection
- Genetic knockdown approaches, such as siRNA/shRNA
- Western blotting and qPCR
- Flow cytometry and immunohistochemistry
- Exosome isolation and purification
- RNA sequencing and gene expression/pathway analyses
- Metabolic profiling
- Chaturvedi et al. (2020) A Novel Combination Approach Targeting an Enhanced Protein Synthesis Pathway in MYC-driven (Group 3) Medulloblastoma. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics. 19:1351-1362. (Corresponding author)
- Chaturvedi et al. (2019) Role of Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5 in Group 3 (MYC-driven) Medulloblastoma. BMC Cancer. 19:1056. (Corresponding author)
- Chaturvedi et al. (2018) Improved therapy for medulloblastoma: targeting hedgehog and PI3K-mTOR signaling pathways in combination with chemotherapy. Oncotarget. 9:16619-16633. (Corresponding author)
- Chaturvedi et al. (2016) Improved Therapy for Neuroblastoma Using a Combination Approach: Superior Efficacy with Vismodegib and Topotecan. Oncotarget. 7:15215-29.
- Chaturvedi et al. (2013) Novel Treatment for Therapy-Resistant Mantle Cell Lymphoma by NF-κB and mTOR Dual Targeting Approach. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics. 12:2006-17.