Interesting Pathology
A Tale of Two Fungi
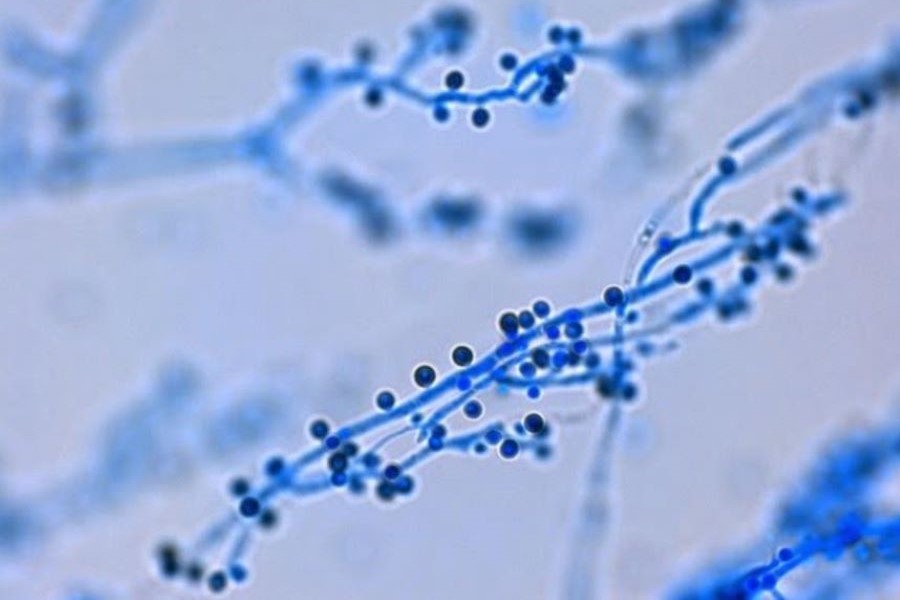
Wet mount of fungal organism
Sporothrix is a member of the thermally dimorphic fungi. These organisms are characterized by growth in a yeast form at 37°C and growth as a mould when cultured at 25°C. Clinically in the United States, the most relivant organisms include Sporothrix schenckii, Histoplasma capsulatum, Blastomyces dermatitides and Coccidioides immitis/posadasii. The later three organisms are generally geographically limited; whereas, S. schenckii is distributed worldwide and is commonly found in association with vegetation. Importantly, these organisms can cause endemic disease in healthy hosts, and the location of exposure can aid diagnosticians in ascribing a causative organism.
The geographically localized fungi typically infect patients through the respiratory tract, after spores located in the soil are inhaled. By contrast, S. schenckii is typically caused by traumatic implantation of spores into soft tissue. Coupled with its association with vegetation, S. schenckii has been ascribed as an affliction of the avid rose gardener.
BioFilm
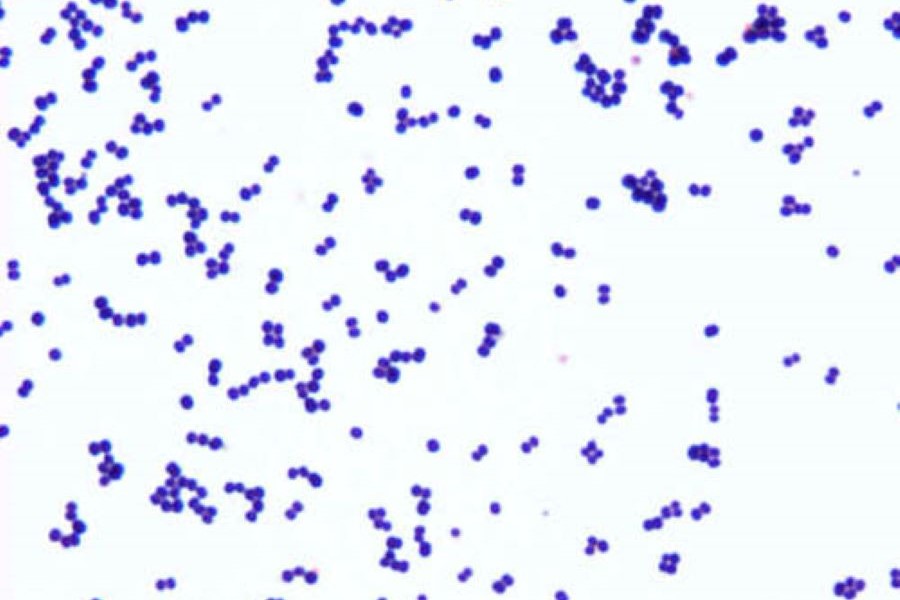
Staphylococcus aureus
35 year old female with intractable headache, neck pain, photophobia, blurry vision, nausea, fevers and chills. Pain is worse with movement/neck flexion.
Infectious work up significant for leukocytosis 16.1. Blood cultures and UA negative. CT head with relatively stable ventricular size, negative for acute hemorrhage or ventriculomegaly.
Four months ago diagnosed with Idiopathic intracranial hypertension and had a VP shunt placed. Symptoms and signs of idiopathic intracranial hypertension are isolated to those produced by increased intracranial pressure (eg, headache, papilledema, double vision, transient visual obscurations, and vision loss). Also at the time there was an elevated ICP with normal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) composition. No other cause of intracranial hypertension evident on neuroimaging or other evaluations.
A lumbar puncture was performed at current presentation and demonstrated an opening pressure of 40 cm H2O. CSF with elevated WBCs (101, predominantly PMN’s), and CSF gram stain positive for gram+ cocci in pairs. The CSF culture grew S. epidermidis.
Catheter associated infections are the most common causes of nosocomial infection. Organisms gain access to the device through 1) invasion of the skin insertion site or 2) contamination of the catheter hub.
- Characteristic flora include coagulase-negative staphylococci and Staphylococcus aureus
- Associated with biofilm formation on the surfaces of indwelling catheters
Biofilm – city of microbes
Components deposited from body fluids are often the first step in biofilm formation – termed conditioning film (fibrin, proteins, electrolytes, organic molecules). Bacteria will then bind to surface proteins and secrete polysaccharide matrix. Other species of bacteria may move into the biofilm and produce different microenvironments within a given biofilm. Under unfavorable environmental conditions, such as exhaustion of nutrients or overcrowding, organisms can detach and become free-floating.
Biofilms have major medical significance for two reasons:
- biofilms decrease susceptibility to antimicrobial agents – impaired diffusion, proximity of bacteria can facilitate plasmid mediated resistance
- microbiology results based on floating organisms may not apply to organisms embedded within a biofilm.
Prevention strategies:
- Maximal sterile barriers during catheter insertion
- Antimicrobial-impregnated catheters
- Removing catheters as soon as the device is no longer essential to patient care
Gross Images
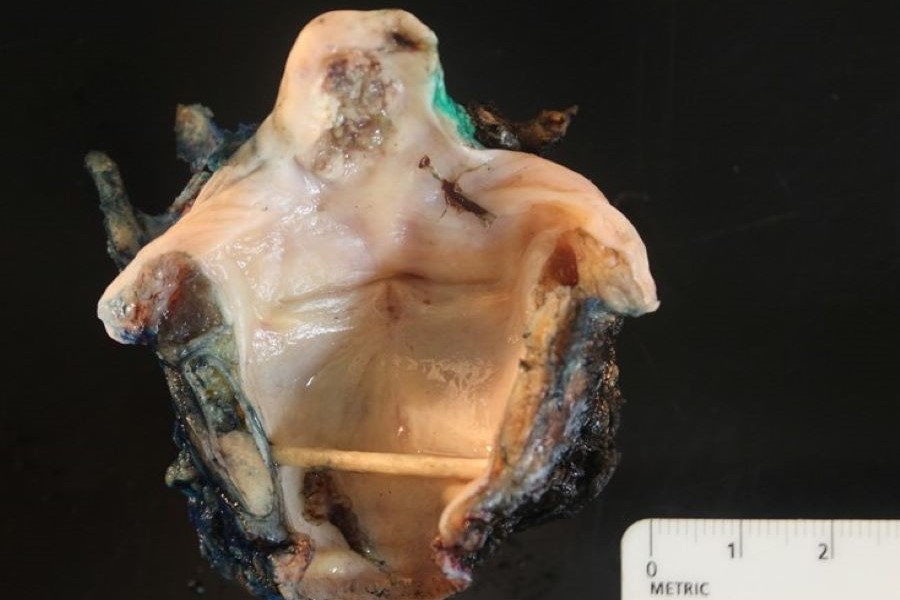
Laryngectomy
The image represents a laryngectomy specimen where the larynx has been opened along the posterior aspect of the trachea. The subglottic mucosa and the true and false vocal cords are unremarkable. In the area of the epiglottis (suraglottic), there is a tan mass measuring 1.7 cm in greatest dimension that has disrupted the mucosal surface and is consistent with a squamous cell carcinoma.
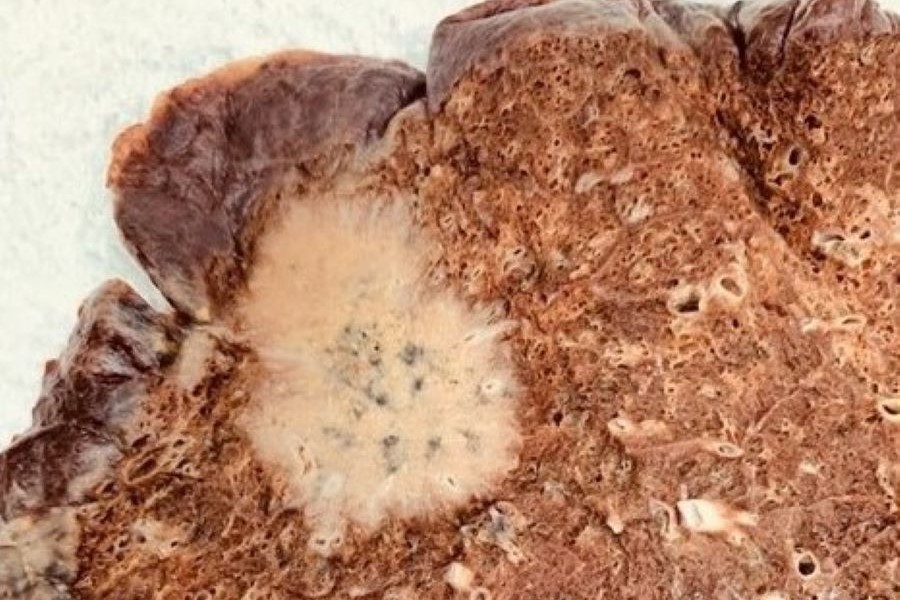
Lung SCC
83 year old man with history of smoking. The 4 cm mass is in the right upper lobe of the lung. Microscopic examination of the tumor was consistent with a squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). Classically, SCC is viewed as a more commonly occurring centrally within the lung. As this case demonstrates, however, it can occur more peripherally. In one small series of cases, 55% of SCC occurred peripherally.