Category: Published Research
Relative efficacy of masks and respirators as source control for viral aerosol shedding from people infected with SARS-CoV-2: a controlled human exhaled breath aerosol experimental study
The Lancet Background Tight-fitting masks and respirators, in manikin studies, improved aerosol source control compared to loose-fitting masks. Whether this translates to humans is not known. Methods We compared efficacy of masks (cloth and surgical) and respirators (KN95 and N95) as source control for SARS-CoV-2 viral load in exhaled breath of volunteers with COVID-19 using […]
Jun 5, 2024
Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Virus Infection in a Dairy Farm Worker
NEJM Sporadic human infections with highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) A(H5N1) virus, with a wide spectrum of clinical severity and a cumulative case fatality of more than 50%, have been reported in 23 countries over more than 20 years.1 HPAI A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b viruses have spread widely among wild birds worldwide since 2020–2021,2,3 resulting in outbreaks in […]
May 7, 2024
Highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) virus in a common bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) in Florida
Nature Since late 2021, highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) viruses of A/goose/Guangdong/1/1996 (H5N1) lineage have caused widespread mortality in wild birds and poultry in the United States. Concomitant with the spread of HPAI viruses in birds are increasing numbers of mammalian infections, including wild and captive mesocarnivores and carnivores with central nervous system involvement. Here […]
Apr 24, 2024
Large-scale phenotyping of patients with long COVID post-hospitalization reveals mechanistic subtypes of disease
Nature One in ten severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infections result in prolonged symptoms termed long coronavirus disease (COVID), yet disease phenotypes and mechanisms are poorly understood1. Here we profiled 368 plasma proteins in 657 participants ≥3 months following hospitalization. Of these, 426 had at least one long COVID symptom and 233 had fully recovered. […]
Apr 10, 2024
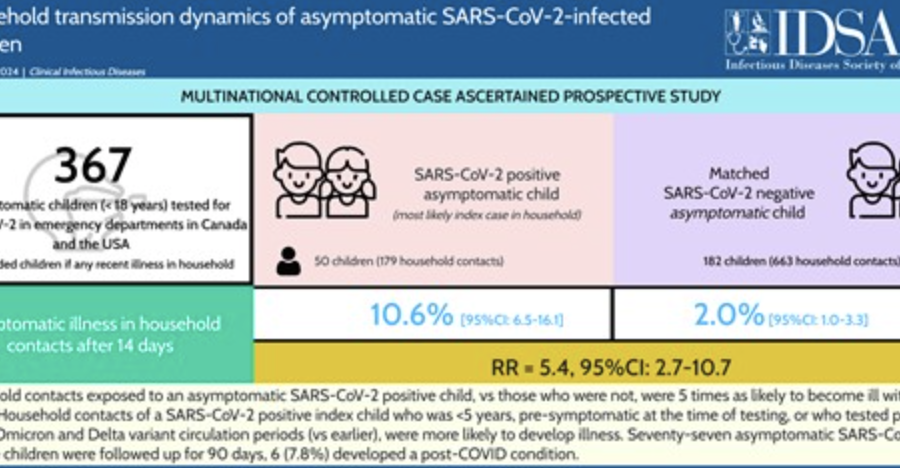
Household Transmission Dynamics of Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2–Infected Children: A Multinational, Controlled Case-Ascertained Prospective Study
Clinical Infectious Diseases Abstract Background Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection in children is highly prevalent but its acute and chronic implications have been minimally described. Methods In this controlled case-ascertained household transmission study, we recruited asymptomatic children <18 years with SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid testing performed at 12 tertiary care pediatric institutions in Canada and the United States. […]
Mar 27, 2024
Ecological countermeasures to prevent pathogen spillover and subsequent pandemics
Nature Substantial global attention is focused on how to reduce the risk of future pandemics. Reducing this risk requires investment in prevention, preparedness, and response. Although preparedness and response have received significant focus, prevention, especially the prevention of zoonotic spillover, remains largely absent from global conversations. This oversight is due in part to the lack […]
Mar 26, 2024
Effectiveness of an Artificial Intelligence–Enabled Intervention for Detecting Clinical Deterioration
JAMA Question Is an artificial intelligence (AI) deterioration model–enabled intervention associated with a decreased risk of escalations in care during hospitalization? Findings In this cohort study of 9938 patients hospitalized at a single academic center in 2021 and 2022, exposure to the intervention was associated with a 10.4–percentage point absolute risk reduction in the primary composite outcome […]
Mar 26, 2024
Proteomic and transcriptomic profiling of brainstem, cerebellum and olfactory tissues in early- and late-phase COVID-19
Nature Neurological symptoms, including cognitive impairment and fatigue, can occur in both the acute infection phase of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and at later stages, yet the mechanisms that contribute to this remain unclear. Here we profiled single-nucleus transcriptomes and proteomes of brainstem tissue from deceased individuals at various stages of COVID-19. We detected an […]
Feb 20, 2024
2020 Ebola virus disease outbreak in Équateur Province, Democratic Republic of the Congo: a retrospective genomic characterization
The Lancet Microbe The Democratic Republic of the Congo has had 15 Ebola virus disease (EVD) outbreaks, from 1976 to 2023. On June 1, 2020, the Democratic Republic of the Congo declared an outbreak of EVD in the western Équateur Province (11th outbreak), proximal to the 2018 Tumba and Bikoro outbreak and concurrent with an outbreak […]
Jan 23, 2024
Fast evolution of SARS-CoV-2 BA.2·86 to JN.1 under heavy immune pressure
The Lancet The SARS-CoV-2 saltation variant BA.2.86, which was quickly designated as a variant under monitoring after its emergence, has garnered global attention. Although BA.2.86 did not show substantial humoral immune escape and growth advantage compared with current dominant variants, such as EG.5.1 and HK.3, it showed remarkably high ACE2 binding affinity. This increased binding […]
Dec 19, 2023