Category: COVID
China will end its COVID-19 quarantine requirement for incoming passengers
(NPR) China will drop a COVID-19 quarantine requirement for passengers arriving from abroad starting Jan. 8, the National Health Commission announced Monday in the latest easing of the country’s once-strict virus-control measures. Currently, arriving passengers must quarantine for five days at a hotel, followed by three days at home. That is down from as much […]
Dec 27, 2022

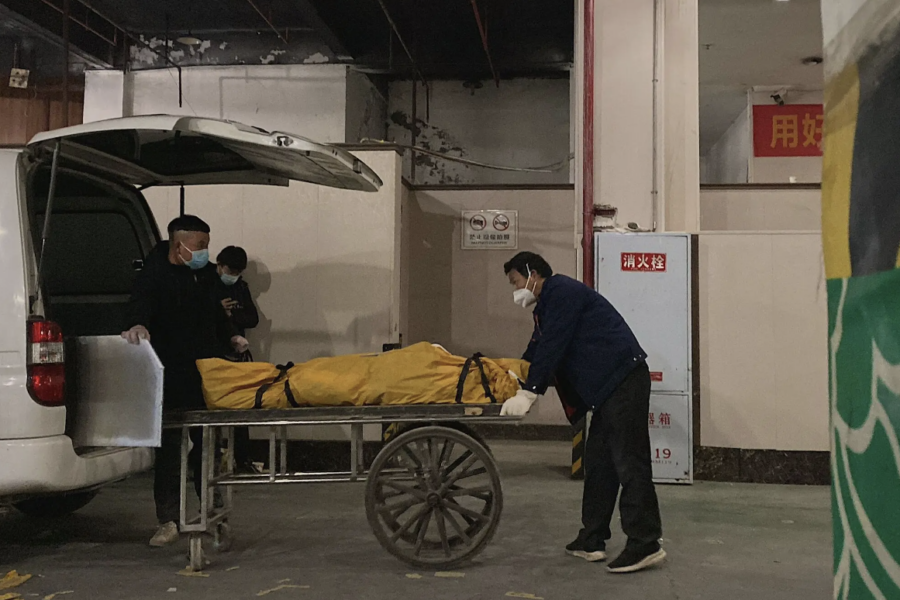
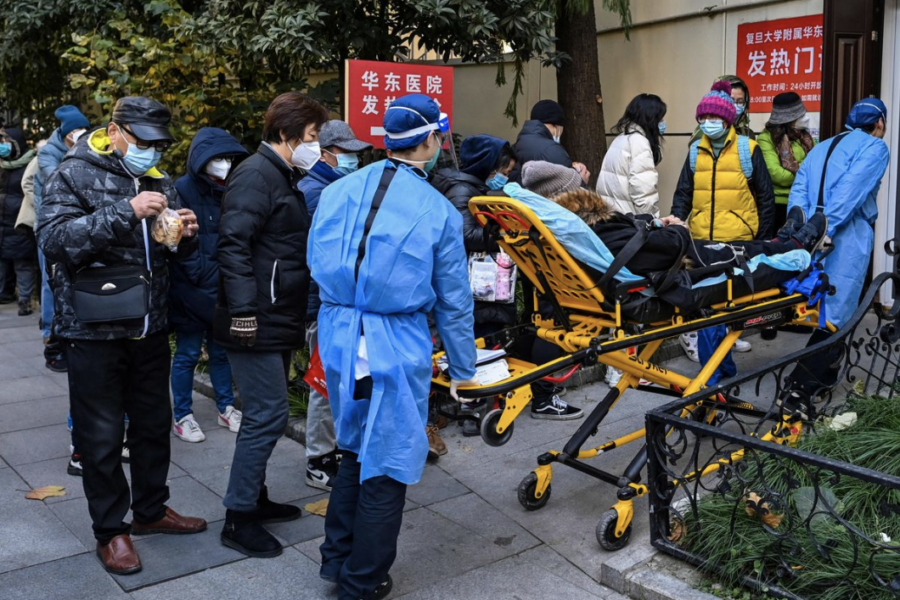
‘Tragic Battle’: On the Front Lines of China’s Covid Crisis
(NYT) Medical staff are outnumbered and working sick as the nation’s health care system buckles under the strain of a spiraling crisis. Slumped in wheelchairs and lying on gurneys, the sickened patients crowd every nook and cranny of the emergency department at the hospital in northern China. They cram into the narrow spaces between elevator […]
Dec 27, 2022

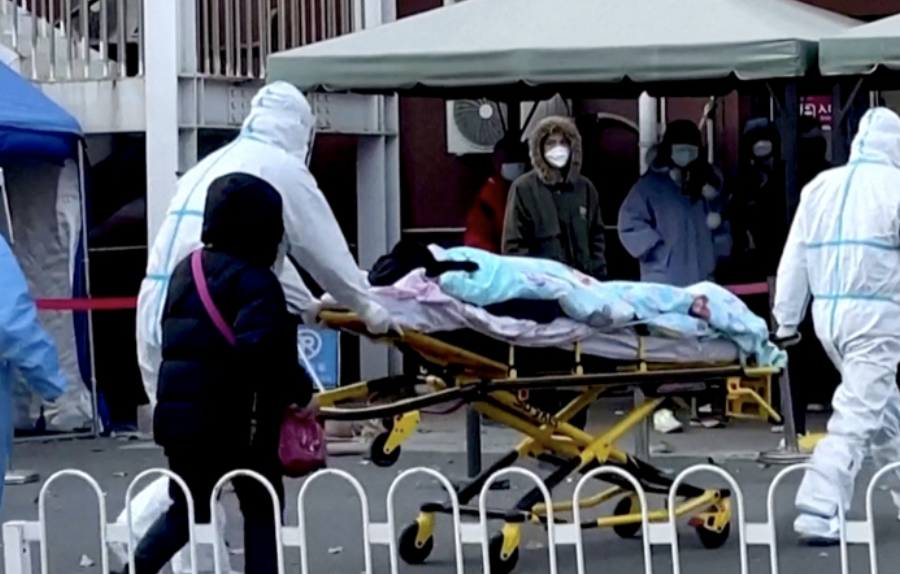
COVID infections surge in Beijing causing hospital shortages
(NPR) AUDIO For nearly three years, China focused on keeping the virus outside of its borders. But now COVID is spreading largely unchecked across the country, leaving hospitals filled and medical resources scarce. In Beijing, so many people are ill, there aren’t enough ambulances. NPR’s Emily Feng brings us this report.
Dec 27, 2022

China’s COVID-19 surge raises odds of new coronavirus mutant
(AP) Could the COVID-19 surge in China unleash a new coronavirus mutant on the world? Scientists don’t know but worry that might happen. It could be similar to omicron variants circulating there now. It could be a combination of strains. Or something entirely different, they say. “China has a population that is very large and […]
Dec 27, 2022
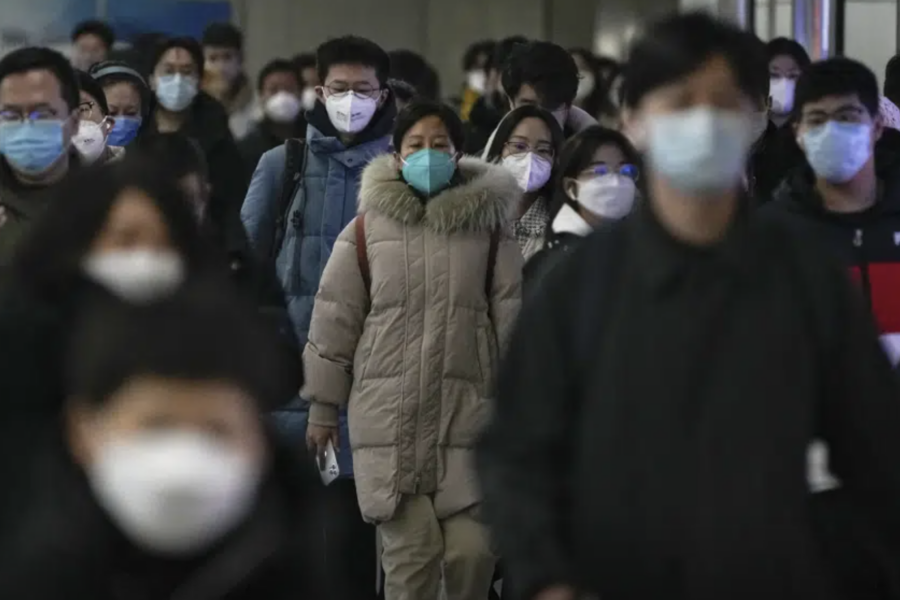

Higher-Dose Steroids Upped Risk of Death in Non-Ventilated COVID-19
(MedPageToday) Higher-dose corticosteroids increased the risk of death in patients with COVID-19 and hypoxia, and who were receiving either no oxygen or simple oxygen only, compared with usual care that included low-dose corticosteroids, an analysis of the randomized RECOVERY trial showed.
Dec 27, 2022
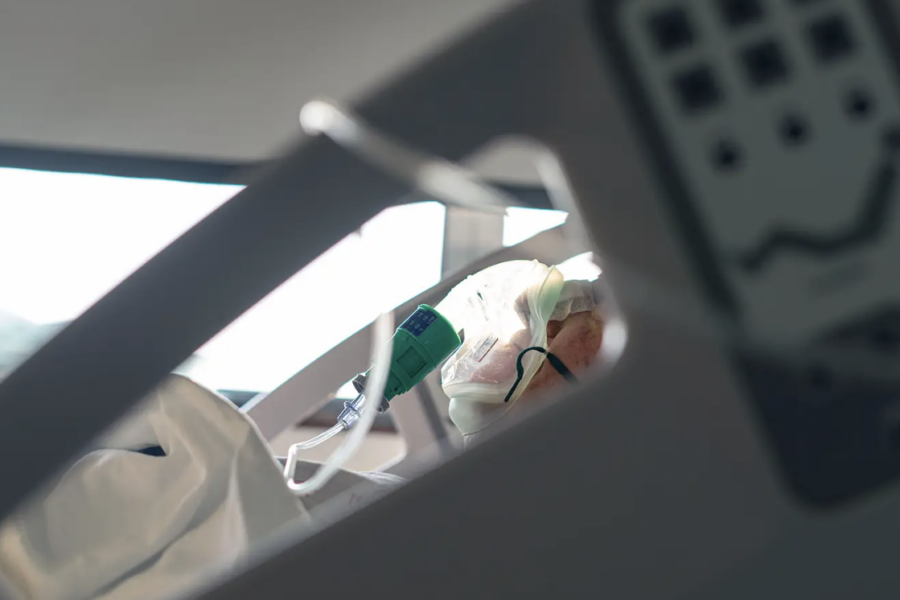

One of our best Covid-19 treatments doesn’t work anymore. What now?
(Vox) Covid-19 is once again trending upward in the United States, with new cases reaching more than 450,000 and deaths climbing up to 3,000 per week. But hospitals will have to face this year’s winter surge without a valuable tool. In late November, the Food and Drug Administration revoked its emergency use authorization for bebtelovimab, a monoclonal antibody […]
Dec 20, 2022
China’s Covid-19 Outbreak Has US Worried About New Variants
(Bloomberg) The US is concerned China’s runaway Covid-19 outbreak might spawn new mutations of the virus, as the world’s most populous country continues to grapple with the impact of loosening “Covid Zero” protocols that had kept the pandemic at bay. “When it comes to the current outbreak in China, we want to see this addressed,” […]
Dec 20, 2022

Are Subphenotypes for Long COVID Beneficial?
(MedPageToday) A recent study opens in a new tab or window published in Nature Medicine, “Data-driven identification of post-acute SARS-CoV-2 infection subphenotypes” by Hao Zhang, PhD, et al. used a data-driven framework to stratify patients suffering with post-acute SARS-CoV-2 (PASC), also referred to as long COVID, into different subcategories of sequelae. The bulk of the patients in the […]
Dec 20, 2022
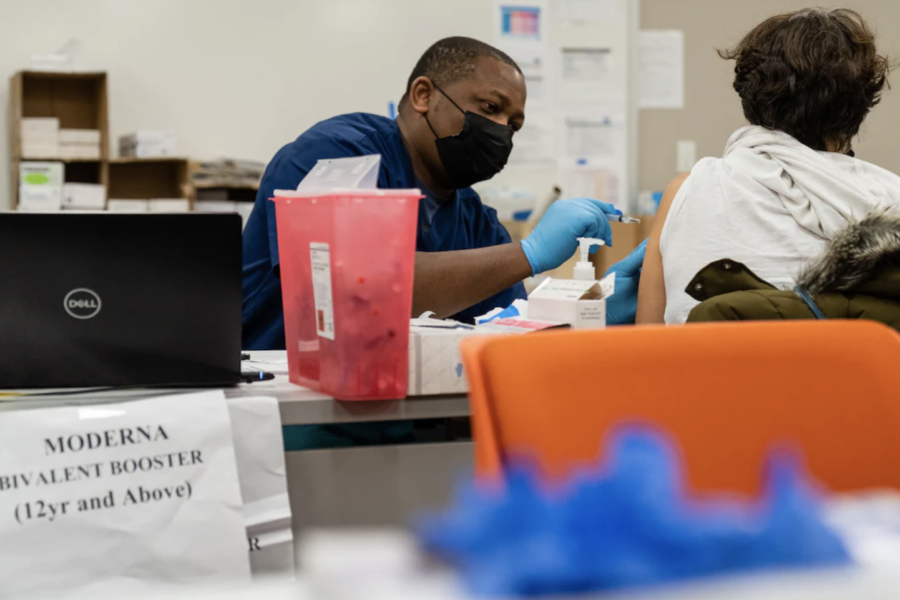
Coronavirus boosters cut hospitalization risk by at least 50%, CDC data shows
(Washington Post) Adults who received the updated coronavirus booster shots are better protected against severe disease than those who haven’t, cutting their risk of having to visit an emergency room or being hospitalized with covid-19 by 50 percent or more,according to new federal data. Two reports released Friday by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention give […]
Dec 20, 2022

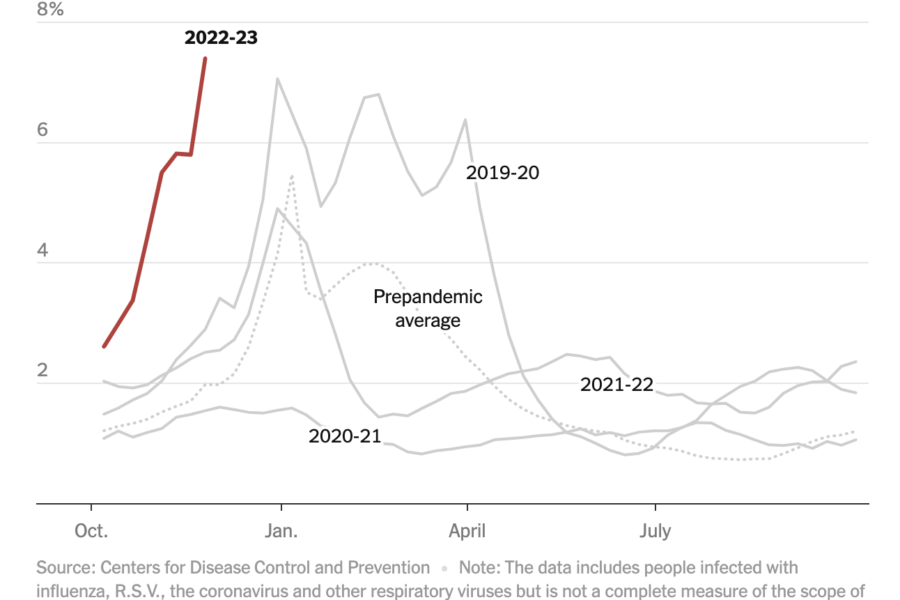
Just How Bad Is the ‘Tripledemic’?
(NYT) After two difficult Covid winters, the current season of respiratory sickness already rivals some of the worst cold and flu seasons on record — and it started about two months early. R.S.V., or respiratory syncytial virus, has made so many young children ill this fall that weekly pediatric hospitalizations for R.S.V. are the highest recorded. Influenza, […]
Dec 16, 2022