Ebola Virus Disease (EVD)
Explore this page for Ebola Virus Disease information, resources, and news.
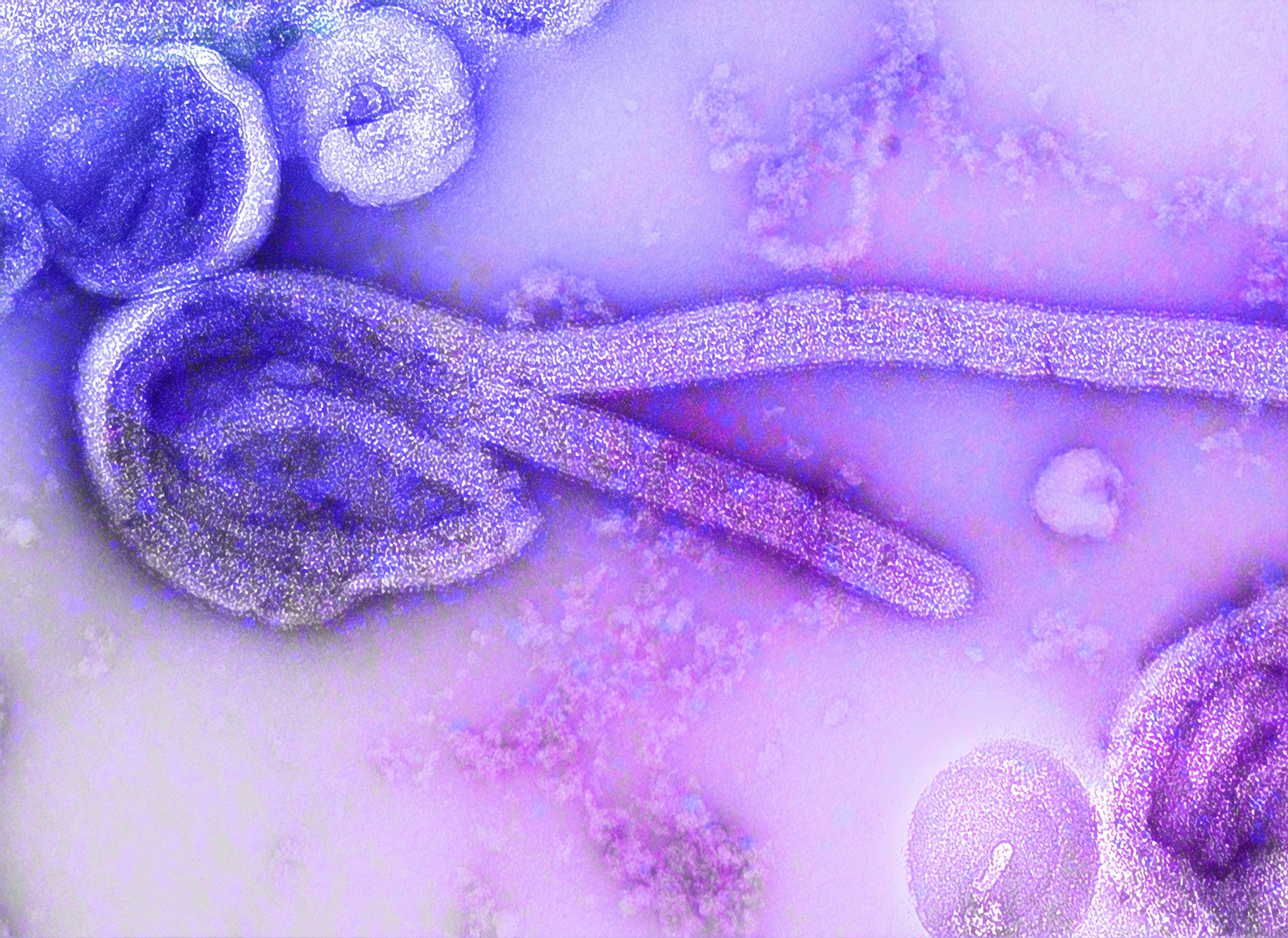
About Ebola Virus Disease
According to the World Health Organization, Ebola virus disease (EVD), previously referred to as Ebola hemorrhagic fever, is a rare yet severe illness in humans, often resulting in fatalities. The transmission of the virus occurs from wild animals to humans and subsequently spreads through human-to-human contact.
Ebola-Sudan Virus Disease
Ebola-Sudan Virus Disease is categorized under the International Classification of Diseases for filoviruses (ICD-11), which was published in May 2019. Outbreaks caused by the Sudan virus are specifically identified as Sudan virus disease (SVD) outbreaks. According to the African Region World Health Organization, Sudan virus disease is notably severe and frequently fatal. First identified in southern Sudan in June 1976, this virus has re-emerged periodically, with seven reported outbreaks attributed to SUDV—four occurring in Uganda and three in Sudan. Historical data indicates that the estimated case fatality ratios for SVD have ranged from 41% to 100% during past outbreaks.