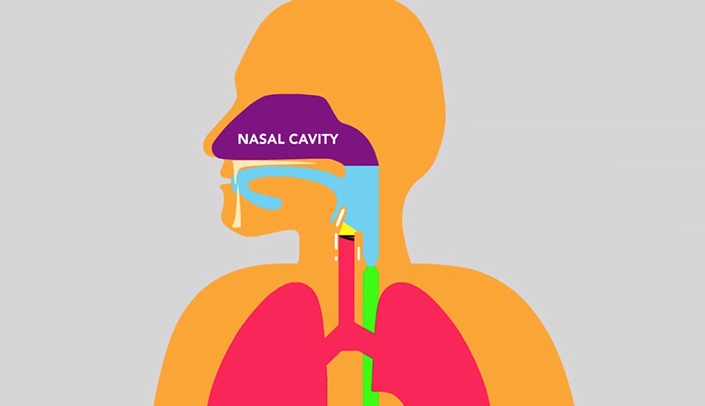
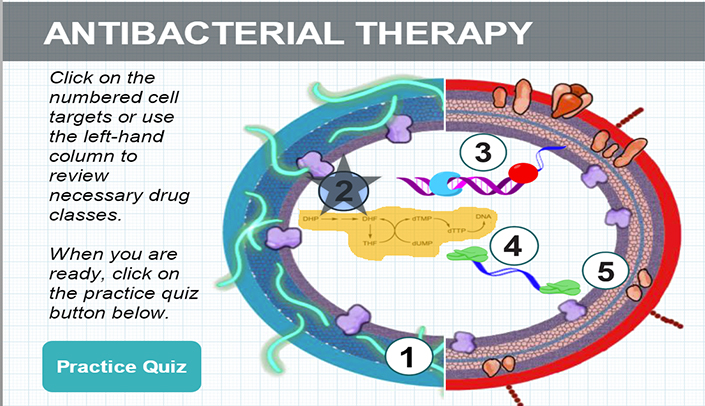
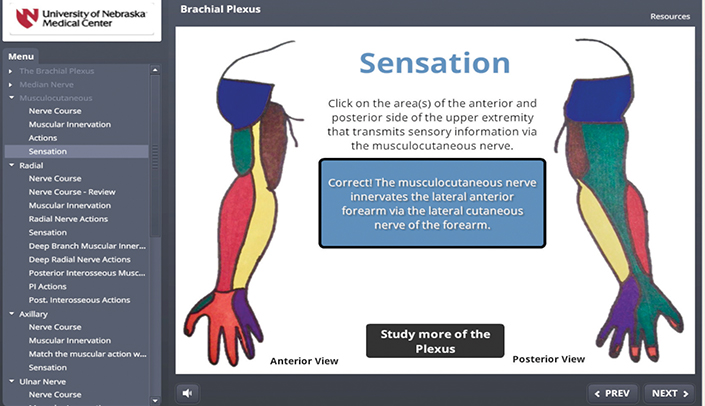
Dysphagia is defined as difficulty swallowing safely or efficiently to meet nutrition and hydration needs. It can result from problems in the neurological system as well as structures within the oral cavity,
pharynx, esophagus, or gastroesophageal junction. While dysphagia can affect individuals of all ages, it most often presents among the elderly and in persons with other medical conditions ranging from prematurity to stroke to cancer. Recognize the role of inter-professional healthcare team members in the screening, evaluation, and management of dysphagia.
Upon completion of this module learners will be able to:
- Describe normal swallowing anatomy and physiology.
- Categorize the types of dysphagia by pathophysiology.
- Recognize the evaluation of dysphagia from screening to invasive procedures.
- Describe the management of dysphagia.
Category: Anatomy, Biology, Chemistry, Physiology
Format: E-Learning Module
Development Date: August 24, 2020
Audience: College of Medicine, Inter-professional
Discipline: Medicine
Permission: This content is available for faculty to use in their course. To show a link to this content, please complete the form below.